
The electron configuration can be visualized as the core electrons, equivalent to the noble gas of the preceding period, and the valence electrons (e.g. It could be part of the main body, but then the periodic table would be rather long and cumbersome.įor atoms with many electrons, this notation can become lengthy and so an abbreviated notation is used. Similarly, the p block are the right-most six columns of the periodic table, the d block is the middle 10 columns of the periodic table, while the f block is the 14-column section that is normally depicted as detached from the main body of the periodic table. Because of this, the first two rows of the periodic table are labeled the s block. The first two columns on the left side of the periodic table are where the s subshells are being occupied. This fact has key implications for the building up of the periodic table of elements.
The ordering of the electrons in the ground state of multielectron atoms, starts with the lowest energy state (ground state) and moves progressively from there up the energy scale until each of the atom’s electrons has been assigned a unique set of quantum numbers. It is the Pauli exclusion principle that requires the electrons in an atom to occupy different energy levels instead of them all condensing in the ground state. In the periodic table, the elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number Z. The number of electrons in each element’s electron shells, particularly the outermost valence shell, is the primary factor in determining its chemical bonding behavior. The configuration of these electrons follows from the principles of quantum mechanics. The chemical properties of the atom are determined by the number of protons, in fact, by number and arrangement of electrons. Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements.Įvery solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. The electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. The periodic table is a tabular display of the chemical elements organized on the basis of their atomic numbers, electron configurations, and chemical properties.

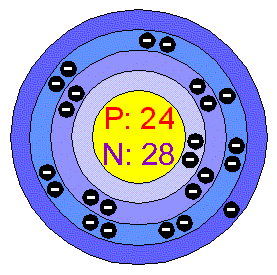
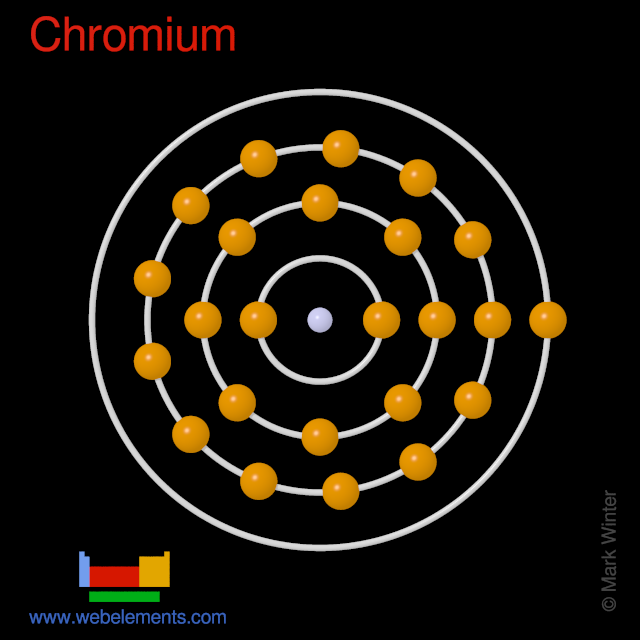
Electron Configuration and Oxidation States of ChromiumĮlectron configuration of Chromium is 3d5 4s1.
#Chromium atomic number free#
The oxidation number of a free element is always 0.You can find examples of usage on the Divide the redox reaction into two half-reactions page. Since the electrons between two carbon atoms are evenly spread, the R group does not change the oxidation number of the carbon atom it's attached to. Unlike radicals in organic molecules, R cannot be hydrogen. Organic compounds can be written in such a way that anything that doesn't change before the first C-C bond is replaced with the abbreviation R (Figure 1c). When dealing with organic compounds and formulas with multiple atoms of the same element, it's easier to work with molecular formulas and average oxidation numbers (Figure 1d). Notice that changing the CH 3 group with R does not change the oxidation number of the central atom. R is an abbreviation for any group in which a carbon atom is attached to the rest of the molecule by a C-C bond. Different ways of displaying oxidation numbers of ethanol and acetic acid.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
